统计一篇英文文章中出现次数最多的10个单词
- package se;
- import java.io.BufferedReader;
- import java.io.File;
- import java.io.FileReader;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Collections;
- import java.util.Comparator;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.Map;
- import java.util.Map.Entry;
- public class damn {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- String str2 = System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir");
- System.out.println(str2);
- long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 程序开始时间
- File file = new File("C:/Users/Wll/Desktop/Computer.txt");
- BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- String line = null;
- while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
- sb.append(line);
- }
- br.close(); // 关闭流
- String words = sb.toString(); // 全部的单词字符串
- String targetString = words.replaceAll("[.,\"\\?!:;\\(\\)]", ""); // 将标点替换为空
- // 分词并且定义英文中不代表实际意义的一些单词,如介词、代词、情态动词等
- String[] singleWord = targetString.split(" ");
- String[] keys = { "you", "i", "he", "she", "me", "him", "her", "it",
- "they", "them", "we", "us", "your", "yours", "our", "his",
- "her", "its", "my", "in", "into", "on", "for", "out", "up",
- "down", "at", "to", "too", "with", "by", "about", "among",
- "between", "over", "from", "be", "been", "am", "is", "are",
- "was", "were", "whthout", "the", "of", "and", "a", "an",
- "that", "this", "be", "or", "as", "will", "would", "can",
- "could", "may", "might", "shall", "should", "must", "has",
- "have", "had", "than" };
- // 将一部分常见的无意义的英语单词替换为字符 '#' 以便后面输出单词出现次数时的判断
- for (int i = 0; i < singleWord.length; i++) {
- for (String str : keys) {
- if (singleWord[i].equals(str))
- singleWord[i] = "#";
- }
- }
- // 将单词以及其出现的次数关联起来
- for (int i = 0; i < singleWord.length; i++) {
- count++; // 计算单词个数
- if ((wordMap.get(singleWord[i]) != null)) {
- int value = ((Integer) wordMap.get(singleWord[i])).intValue();
- value++;
- wordMap.put(singleWord[i].toLowerCase(), new Integer(value)); // 将单词转换为小写存放以统一格式
- } else {
- wordMap.put(singleWord[i].toLowerCase(), new Integer(1));
- }
- }
- System.out.println("\t\t--文件信息--");
- System.out.println(" 名称: " + file.getName() + " 大小: "
- + file.length() / 1024 + " KB");
- System.out.println("\t\t--文件信息--");
- System.out.println();
- System.out.println("■■■■ " + count + " 个单词中出现频率最高的 10 个单词如下■■■■");
- // 比较器, 按值排序
- System.setProperty("java.util.Arrays.useLegacyMergeSort", "true");
- List<Entry<String, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Entry<String, Integer>>(
- wordMap.entrySet());
- Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Entry<String, Integer>>() {
- public int compare(Entry<String, Integer> e1,
- Entry<String, Integer> e2) {
- if (e2.getValue() != null && e1.getValue() != null
- && e2.getValue().compareTo(e1.getValue()) > 0) {
- return 1;
- } else {
- return -1;
- }
- }
- });
- int wordCount = 1; // 记录已经输出单词的个数
- for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : list) {
- if (entry.getKey().equals("#")) // 相当于过滤作用,不输出介词、代词、情态动词等无意义单词
- continue;
- System.out.printf("\t%2d、 %8s \t %4d次\n", wordCount,
- entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
- if (wordCount++ == 10) { // 表示只输出10个
- long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 程序结束时间
- System.out.println("■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■ 耗时 " + (end - start)
- + " ms" + " ■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■");
- return;
- }
- }
- }
- private static HashMap<String, Integer> wordMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
- private static int count = 0;
- }
程序运行情况如下:
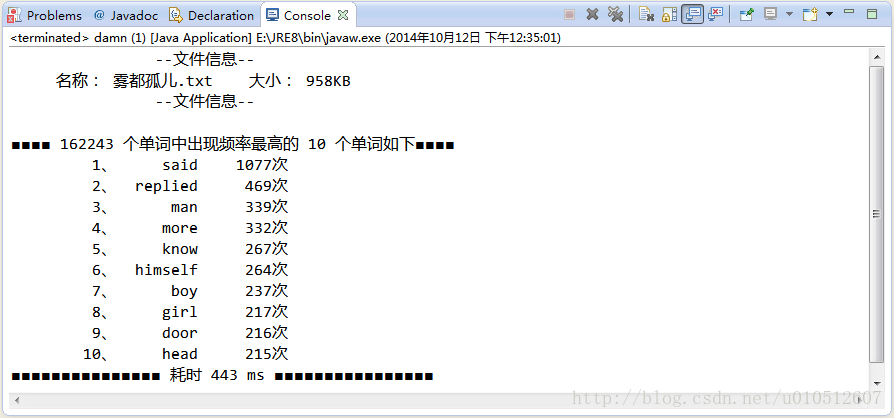
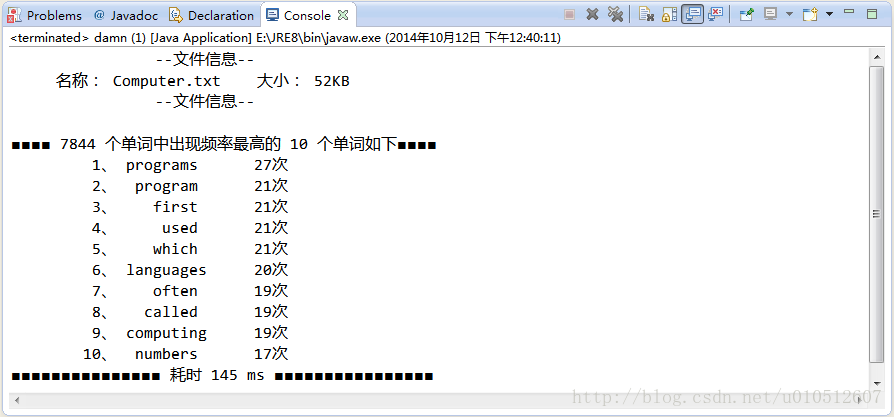
总的来说,这个程序自己觉得还是完成得比较好,而且从中也学到了很多。比如正则表达式之前没怎么接触过,这次就学习了许多正则表达式相关的知识。另外,也进一步熟悉了HashMap类和ArrayList类。除此之外,还学到了一些编写程序的方法与技巧,使得代码条理更加清晰。